Over the past few years, things have changed in the collaboration space. Historically we were all On-premises and behind the corporate firewall, now however we either live in the cloud only world or the hybrid space. The companies that create the technology have had to adapt to make sure their services and components are viable options when looking at what to use.
This shift has come based on the idea of either “Software as a Service” or “Platform as a Service”. These two phrases now determine what we should do. Understanding them is important to being able to choose the right solution for your organization.
Let us understand what Cloud Computing means. In simple terms, cloud is a complex infrastructure technology comprising of servers, databases and computers. These are connected together and can be shared by multiple users based on access permissions. Typically, cloud services have following characteristics:
- User is able to avail the services fairly quickly as compared to traditional IT by simply signing up for the services.
- User is able to access the service via multiple platforms such as laptop, desktop, mobile etc.
- The resources (computers, databases and servers) are shared across multiple users
- There is scalability and flexibility to increase capacity as the demand increases
- Metered billing based on the actual usage which is delivered automatically
Now with that understanding, let’s look at what SaaS and PaaS really are.
Software as a Service
Software as a service (SaaS) is a software licensing and delivery model in which software is licensed on a subscription basis and is centrally hosted. It is sometimes referred to as "on-demand software", and was formerly referred to as "software plus services" by Microsoft. SaaS is typically accessed by users using a thin client via a web browser. SaaS has become a common delivery model for many business applications, including office and messaging software, payroll processing software, DBMS software, management software, CAD software, development software, gamification, virtualization, accounting, collaboration, customer relationship management (CRM), Management Information Systems (MIS), enterprise resource planning (ERP), invoicing, human resource management (HRM), talent acquisition, content management (CM), and service desk management. SaaS has been incorporated into the strategy of nearly all leading enterprise software companies. - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_as_a_service
Advantages of SaaS
Gain access to sophisticated applications. To provide SaaS apps to users, you don’t need to purchase, install, update, or maintain any hardware, middleware, or software. SaaS makes even sophisticated enterprise applications, such as ERP and CRM, affordable for organizations that lack the resources to buy, deploy, and manage the required infrastructure and software themselves:
- Pay only for what you use. You also save money because the SaaS service automatically scales up and down according to the level of usage.
- Use free client software. Users can run most SaaS apps directly from their web browser without needing to download and install any software, although some apps require plugins. This means that you don’t need to purchase and install special software for your users.
- Mobilize your workforce easily. SaaS makes it easy to “mobilize” your workforce because users can access SaaS apps and data from any Internet-connected computer or mobile device. You don’t need to worry about developing apps to run on different types of computers and devices because the service provider has already done so. In addition, you don’t need to bring special expertise onboard to manage the security issues inherent in mobile computing. A carefully chosen service provider will ensure the security of your data, regardless of the type of device consuming it.
- Access app data from anywhere. With data stored in the cloud, users can access their information from any Internet-connected computer or mobile device. And when app data is stored in the cloud, no data is lost if a user’s computer or device fails.
Platform as a Service
Platform as a service (PaaS) or application platform as a service (aPaaS) is a category of cloud computing services that provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure typically associated with developing and launching an app. PaaS can be delivered in two ways: as a public cloud service from a provider, where the consumer controls software deployment with minimal configuration options, and the provider provides the networks, servers, storage, operating system (OS), 'middleware' (e.g. Java runtime, .NET runtime, integration, etc.), database and other services to host the consumer's application; or as a private service (software or appliance) inside the firewall, or as software deployed on a public infrastructure as a service. - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Platform_as_a_service
Advantages of PaaS
By delivering infrastructure as a service, PaaS offers the same advantages as IaaS. But its additional features—middleware, development tools, and other business tools—give you more advantages:
- Cut coding time. PaaS development tools can cut the time it takes to code new apps with pre-coded application components built into the platform, such as workflow, directory services, security features, search, and so on.
- Add development capabilities without adding staff. Platform as a Service components can give your development team new capabilities without your needing to add staff having the required skills.
- Develop for multiple platforms—including mobile—more easily. Some service providers give you development options for multiple platforms, such as computers, mobile devices, and browsers making cross-platform apps quicker and easier to develop.
- Use sophisticated tools affordably. A pay-as-you-go model makes it possible for individuals or organizations to use sophisticated development software and business intelligence and analytics tools that they could not afford to purchase outright.
- Support geographically distributed development teams. Because the development environment is accessed over the Internet, development teams can work together on projects even when team members are in remote locations.
- Efficiently manage the application lifecycle. PaaS provides all of the capabilities that you need to support the complete web application lifecycle: building, testing, deploying, managing, and updating within the same integrated environment.
Still confused? I hope so, knowing and choosing the right one can be complicated as you really need to know the differences between the two, so that you can make that informed decision.
Compared
When you put these two services side by side, there are many common things, but they are really different.
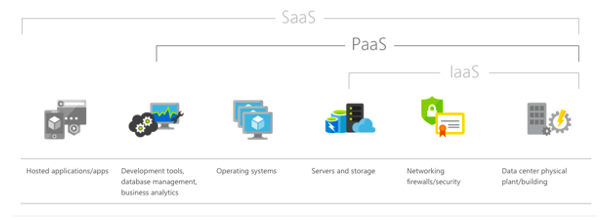
As you can see there is an overlap, but in reality, they are different. The PaaS piece is all about the under-pinning infrastructure, the servers, networking and even the physical location. SaaS is really the application you wish to provide or use which utilizes the core infrastructure underneath.
So, the big question, how does the factor into your cloud strategy for SharePoint? Do you use PaaS or SaaS?
That really comes down to what you want out of the system. Moving infrastructure to the cloud using either model will be an advantage either way. The main different is really down to one is providing you an application or set of services that you use, the other is providing you a data center where you define and create the server infrastructure you need, based on a solid proven infrastructure that you don’t have to worry about. If you are an organization that needs to own the infrastructure still, control at a granular level the operating system upwards then PaaS is the options you need to have. Not only providing this, but also the ability to scale as needed easily, will be the win you need. If you don’t want to worry about servers, patching of any infrastructure, then SaaS is for you. The application is just provided to you, you use what you need and never have to patch a server again!! Surely that is a win? However, that comes as a cost, as you do in some respects lose an element of control and you have to live within the components of the service and rely on someone else to resolve technical issue.
All in all, choosing the right option is important. Working with clients over the past few years, has seen me work on both, some have moved to the cloud (all in), others have stayed with a virtual physical infrastructure and moved to the cloud. Both options work, both have advantages and disadvantages, so choose wisely what you need.





