How to Free up Disk Space on End User Devices
Here's how to free up disk space using some often-overlooked techniques.
November 3, 2021
Computers are equipped with larger hard disks than ever before, but hard disk space--or lack thereof--can still be an issue. This is especially true if a user is working remotely from a personal device. There are many tried-and-true techniques for gaining back disk space, including deleting temporary files, deleting downloaded files, clearing the browser cache and turning on Windows Storage Sense. However, there are some other, often overlooked methods that may help you reclaim more disk space.
Look for Stray Hyper-V Components
I will be the first to admit that most casual users probably aren’t in the habit of creating Hyper-V virtual machines. Even so, if a system is running low on disk space, it may be worth at least checking to see if there are unused virtual machine remnants taking up space on the system. One of the dirty little secrets about Hyper-V is that when you use the Hyper-V Manager to delete a virtual machine, the virtual hard disk is not actually deleted; rather, Windows leaves the virtual hard disk intact in case it is needed in the future. As such, orphaned virtual hard disks can consume a significant amount of disk space.
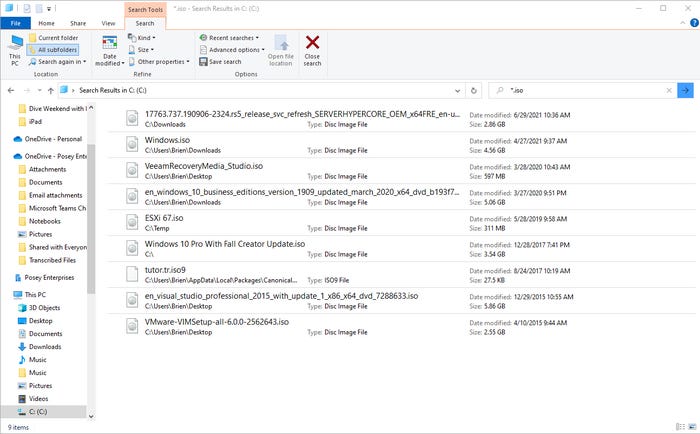
Similarly, the ISO files that are used to install guest operating systems can also consume a lot of hard disk space. The easiest way to check for such files is to open File Explorer, navigate to the root directory, and then enter an asterisk, followed by a period and a file extension into the search box (for example: *.ISO). As you can see in Figure 1, I have several gigabytes of ISO files on my own hard disk. Incidentally, if you want to search for Hyper-V virtual hard disks, those files will usually have an extension of .VHD or .VHDX.
How to free up Disk Space 1
Figure 1
ISO files can consume a lot of disk space.
Enable NTFS Compression
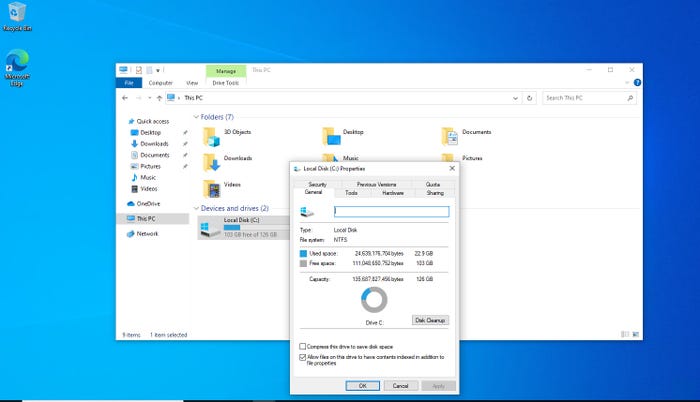
Another way that you might be able to reclaim some disk space is by compressing the disk. To do so, open File Explorer and then right click on the disk and select the Properties command from the shortcut menu. This will cause Windows to display the disk’s properties sheet. Select the General tab and then select the Compress This Drive to Save Disk Space checkbox, as shown in Figure 2. Incidentally, there is also a checkbox that is used to enable file content indexing. Content indexing makes it quicker and easier to search for files that are stored on the system. However, the indexes consume disk space, so you might consider disabling content indexing.
how to free up Disk Space 2
Figure 2
You can compress NTFS disks to save space.
In case you are wondering, deduplication is not officially supported in Windows 10, so using NTFS compression is the best option for reducing the data footprint without resorting to using a third-party product or forcing Windows 10 to use an unsupported configuration.
Disable or Move the Pagefile
The pagefile has been a part of the Windows operating system for decades. The pagefile is optional, but it can consume a significant amount of disk space. There are three main things that the pagefile does:
Allows Windows to use disk storage to make up for RAM shortages
Supports system crash dumps
Supports various Windows Server roles, such as domain controllers, DFS Replication servers, Certificate servers and ADAM/LDS servers
Opinions vary widely among IT professionals as to whether the pagefile should be disabled. In most cases, if a Windows 10 system is stable and it has plenty of memory, it is generally safe to disable the pagefile. (You can find Microsoft’s guidance here.)
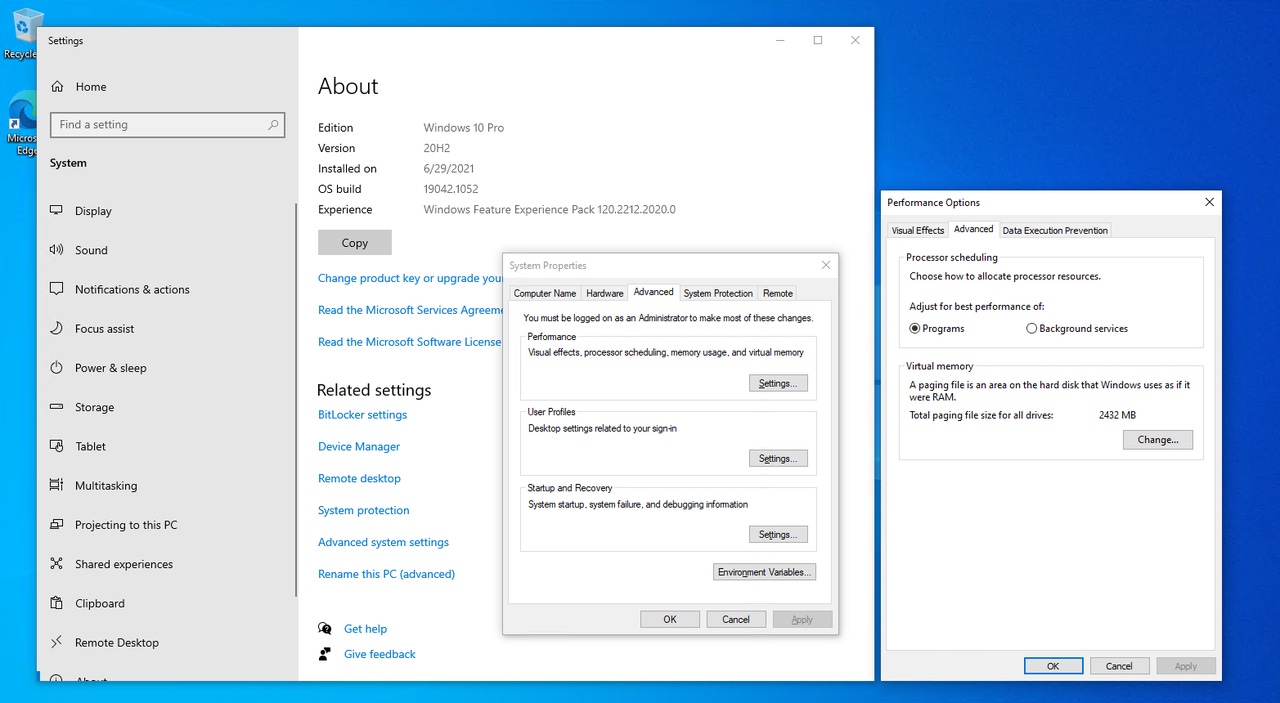
If you decide to disable the pagefile, you can do so by right clicking on the Start button and then clicking on System. When the System Settings page appears, select the About tab, scroll to the bottom, and then click on the Advanced System Settings link. This will cause Windows to display the System Properties sheet. Select the properties sheet’s Advanced tab and then click on the Settings button within the Performance section. This will cause Windows to open the Performance Options dialog box. Select this dialog box’s Advanced tab and then click the Change button to disable, resize or move the pagefile. As you can see in Figure 3, this particular system’s pagefile is consuming 2 GB of storage space.
how to free up Disk Space 3
Figure 3
The pagefile can consume a lot of space.
Disable Hibernation
One last technique for reclaiming some disk space is to disable hibernation. This works because when a computer goes into hibernation, its memory contents are written to disk. With that said, it may not be a good idea to disable hibernation on laptops because Windows may use hibernation as a way of saving the machine’s state just before the battery goes dead.
The easiest way to disable hibernation is to open an administrative Command Prompt window and enter the following command:
Powercfg /h offYou can see what this looks like in Figure 4.
how to free up Disk Space 4
Figure 4
This is how to disable Windows hibernation.
About the Author
You May Also Like








.jpg?width=700&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
